I PCB sono ampiamente utilizzati in varie famiglie, industriale, militare, e attrezzature automobilistiche. Al fine di garantire il funzionamento dell'apparecchiatura e prolungarne la durata, è fondamentale garantire che i circuiti stampati e componenti sulla scheda sono protetti da ogni pericolo, poiché qualsiasi errore in essi contenuto può influire sulle prestazioni del dispositivo o addirittura causare il guasto dell'intero dispositivo. Il rivestimento PCB è un modo molto efficace per proteggere il PCB.
In questa guida definitiva, esamineremo tutto ciò che devi sapere sui rivestimenti PCB 2023 – dalle tipologie di materiali ai metodi di applicazione e agli standard di qualità. Con la giusta strategia di rivestimento, puoi prolungare significativamente la vita operativa dei PCB nei tuoi prodotti. Iniziamo!
Cos'è il rivestimento PCB?
Il rivestimento PCB è una tecnologia che protegge il PCB da fattori sfavorevoli come la corrosione, umidità, e shock fisici applicando uno strato sottile e non conduttivo sulla superficie del circuito stampato e dei componenti elettronici. Con rivestimento del circuito stampato, si riduce la possibilità di guasto del circuito del PCB e dei componenti elettronici, e anche la vita utile del prodotto elettronico finale può essere estesa.
Tipi di rivestimento PCB
In termini di materiali utilizzati, I rivestimenti PCB possono essere suddivisi in cinque tipi:
- Acrilico: facile da applicare e riparare, caratterizzato da una buona protezione dall'umidità e dall'abrasione, e buona resistenza meccanica. Ma questo tipo di rivestimento ha una scarsa resistività ai solventi e una scarsa resistenza alla temperatura.
- Poliuretano – come l'acrilico, fornisce un'eccellente resistenza all'umidità e all'abrasione, Inoltre, fornisce una migliore resistenza ai solventi. Il lato negativo, tuttavia, è che il rivestimento è difficile da rimuovere.
- Epossidico: ha un'eccellente resistenza meccanica e può offrire una buona protezione dall'abrasione e dall'umidità. Ma i rivestimenti epossidici hanno scarsa flessibilità e resistenza alla temperatura e sono difficili da riparare.
- Silicone: questo tipo di rivestimento è disponibile con polimerizzazione dell'umidità, Cura UV, e cura del calore, ha un'ottima resistenza alla temperatura e all'umidità, ma ha scarse prestazioni in termini di resistività all'abrasione e resistenza meccanica.
- Paralyene: i rivestimenti in paralyene sono disponibili per qualsiasi superficie, che è un'opzione perfetta per i dispositivi utilizzati nelle applicazioni aerospaziali e mediche, in quanto possono proteggere i PCB dai solventi organici, reagenti inorganici, e acidi. Il loro svantaggio è che sono difficili da rielaborare.
 Scegliere il giusto materiale di rivestimento per PCB
Scegliere il giusto materiale di rivestimento per PCB
Ora che comprendiamo le proprietà dei diversi rivestimenti PCB, quindi quali fattori dobbiamo considerare per scegliere il rivestimento più adatto al tuo progetto? Bene, di seguito abbiamo elencato alcune considerazioni chiave:
- Ambiente operativo
Temperatura – Se il PCB sarà esposto a temperature elevate, rivestimenti come silicone o poliuretano sono più adatti degli acrilici. Per ambienti con temperature molto basse, il parilene eccelle.
Umidità – Se la resistenza all'umidità è fondamentale, il parylene e alcuni uretani forniscono la migliore protezione contro la trasmissione e l'assorbimento del vapore acqueo.
Chimico – Per ambienti chimici corrosivi, parilene e uretano hanno generalmente le migliori proprietà di barriera chimica.
Esposizione ai raggi UV – Gli acrilici hanno una buona resistenza ai raggi UV. Anche i siliconi e il parilene possono resistere ai raggi UV.
- Proprietà elettriche
Rigidità dielettrica – Questo dovrebbe superare la tensione massima che le tracce del PCB trasporteranno. Parylene e silicone hanno elevata rigidità dielettrica.
Resistenza di isolamento – Un valore di megaohm più alto indica un migliore isolamento elettrico. Importante per evitare correnti di dispersione.
Conduttività termica – Capacità di dissipare il calore. Fondamentale per l'elettronica di potenza. I rivestimenti in silicone offrono la migliore conduttività termica.
- Proprietà meccaniche
Durezza – I rivestimenti più duri come quelli epossidici e alcuni uretani forniscono una maggiore resistenza ai graffi/all'abrasione.
Flessibilità – I rivestimenti in silicone e parilene mantengono la flessibilità, importante per i circuiti di flessione dinamica.
Adesione – Proprietà come la chimica della superficie determinano quanto bene un rivestimento si lega al Substrato PCB.
- Costo
I costi del rivestimento delle schede PCB sono determinati da fattori come la chimica delle materie prime, esigenze delle apparecchiature di elaborazione, tempi di produzione, complessità dell'applicazione, spessore del rivestimento, capacità di riparazione, e volume. In generale, l'analisi dei costi valuta le spese del materiale di rivestimento e del processo di applicazione rispetto ai requisiti prestazionali e alle condizioni operative dell'applicazione finale. Valutare fattori come la compatibilità dei materiali, metodo di lavorazione, e l'affidabilità mirata nel tempo consente la scelta del rivestimento più conveniente che soddisfi comunque le esigenze tecniche.
Processo di rivestimento PCB
L'applicazione di un rivestimento protettivo ai circuiti stampati richiede un'attenta preparazione, applicazione, curare, e test:
- Preparazione della superficie
I pannelli devono essere puliti accuratamente prima del rivestimento per favorire l'adesione. Le tecniche comuni includono la pulizia con solvente e i trattamenti superficiali al plasma/corona.

- Applicazione del rivestimento
Esistono diversi metodi per applicare il rivestimento dei circuiti stampati, sono:
- Spruzzatura manuale
Questo metodo è adatto per cicli di produzione a basso volume poiché è un processo che richiede tempo. Normalmente, utilizziamo una bomboletta spray o una pistola a spruzzo portatile per applicare il rivestimento, e prima di spruzzare, quelle aree che non necessitano di rivestimento devono essere coperte. Gli effetti del rivestimento sarebbero leggermente diversi tra i diversi lotti a causa dell'operazione manuale.
- Rivestimento selettivo
Si riferisce a un processo di rivestimento automatico che applica un rivestimento alle aree specifiche sui circuiti stampati utilizzando ugelli di spruzzatura robotizzati programmati, e non è necessario coprire le aree che non devono essere spruzzate. Questo processo è caratterizzato da alta efficienza e precisione, adatto per produzioni ad alto volume.
- Immersione
Per questo metodo, I PCB verrebbero prima immersi nella soluzione di rivestimento e poi ritirati. Molti fattori influenzerebbero l'effetto del rivestimento come l'immersione e la velocità di ritiro, tempo di immersione, eccetera. È necessaria un'ampia mascheratura prima del processo di rivestimento, quindi è adatto per quei PCB che richiedono un rivestimento su entrambi i lati.
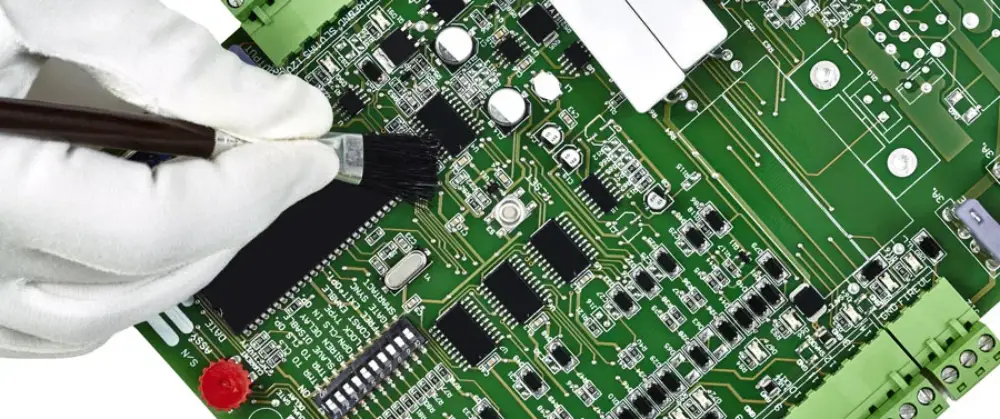
- Spazzolatura
Un pennello viene utilizzato per applicare un rivestimento su aree specifiche, ed è un metodo utilizzato principalmente per la riparazione e la rilavorazione. Il processo richiede molto tempo e richiede molto lavoro, l'effetto del rivestimento finale dipende dalla competenza dell'operatore.
- Stagionatura/essiccazione
I metodi di polimerizzazione comuni includono la polimerizzazione termica, Cura UV, e cura dell'umidità. Rigorosi controlli del processo durante la polimerizzazione sono fondamentali per garantire che i rivestimenti reticolino completamente senza diventare eccessivamente fragili. Il metodo di polimerizzazione viene selezionato per adattarsi alla chimica del polimero e soddisfare le esigenze di efficienza e prestazioni.
- analisi
Il test è una fase importante per verificare l'intervallo di prestazioni e i limiti del rivestimento isolato del circuito in varie condizioni ambientali per ottenere le caratteristiche desiderate.
Un rivestimento ideale ha una caratteristica di adesione eccessiva, buone proprietà elettriche, e caratteristiche fisiche con bassa umidità. Questi test per il test del rivestimento coinvolgono sia test di base che avanzati. Primo, il test di base controlla l'umidità accelerata e le prestazioni elettriche. Secondo, test avanzati controllano la nebbia salina, rapido cambiamento ambientale, e il limite di temperatura.
PCB Asse Standard di rivestimento
Nel rivestimento conforme, esistono una serie di standard di rivestimento PCB che ne richiedono l'utilizzo in determinate condizioni, come in ambito militare, automobile, uso domestico, eccetera. Più comunemente i rivestimenti conformi si qualificano per le specifiche MIL-I-46058C o IPC-CC-830B che si riferiscono strettamente a MIL-I-46058C.
MIL-I-46058C: Uno standard di rivestimento conforme comune nel settore, noto anche come composto isolante militare. Richiede test da qualsiasi laboratorio autorizzato MIL e da allora è ancora utilizzato anche dopo la disattivazione 1998 per nuovi design. Questo test richiede un elenco di prodotti qualificati standard (QPL).
Def Stan 59/47: Uno standard simile al 46058C utilizzato per il rivestimento di dispositivi di fascia alta per uso militare, ma il Ministero della Difesa britannico deve prima approvarli.
IEC 61086: Uno standard basato sull'autocertificazione del fornitore con requisiti simili a 46058c. La Commissione Elettrotecnica Internazionale lo governa.
IPC-CC-830B: Standard utilizzato attivamente e continuamente aggiornato simile al 46058C, introdotto quando 46058C rimane inattivo. Materiale standardizzato per 46058C che segue queste specifiche. Nessun test è disponibile poiché non viene mantenuto alcun QPL.
UL94V0: Si riferisce alla proprietà di rivestimento conforme dell'autoestinguente su un substrato FR4. V0 è la categoria più alta ottenibile con V1 e V2 come successori.