PCB delamination is a serious defect in printed circuit boards, where internal layers separate and compromise the structural and electrical integrity. It can cause reliability problems if it’s not caught early on. Thus, we should know the factors that lead to PCB delamination and methods to prevent such an issue. This article explains what PCB delamination is, its common causes, and prevention methods. Let’s dive right in.
What Is PCB Delamination?
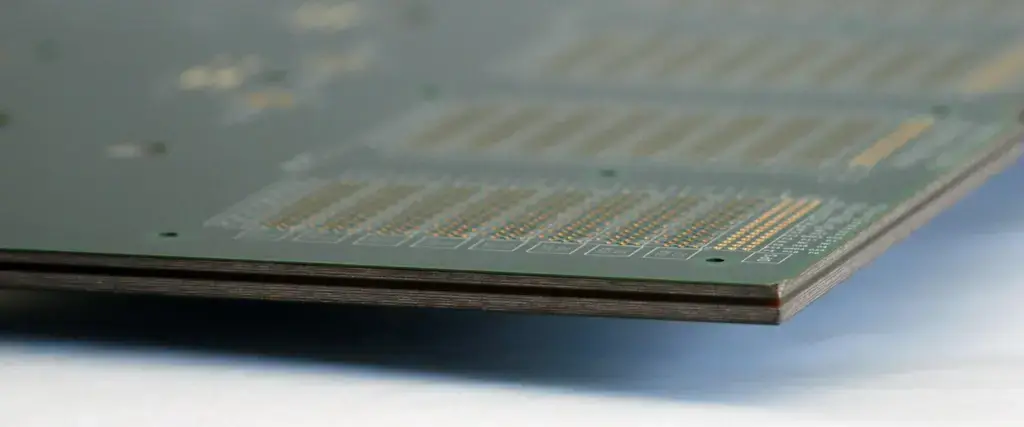
PCB delamination refers to the separation between the laminated layers of fiberglass and resin within a PCB. In most PCBs, FR-4 is used as the base material, which is composed of woven glass fibers bonded with epoxy resin. In the case of delamination, the resin-fiber bond is degraded, resulting in the epoxy resin separating from the glass fibers, or results in separation between adjacent laminate layers.
This separation disrupts electrical connectivity and PCB functioning. Cracks fracture the thin copper traces between layers, interrupting circuits. Further delamination can also lead to short circuits between previously insulated layers.
This defect can manifest as obvious holes or blisters on the PCB surface, although in some cases, delamination is internal and may only be detected by X-ray analysis. It’s worth noting that delamination is more frequent in multilayer PCBs with complex designs since they contain multiple bonded interfaces between layers.
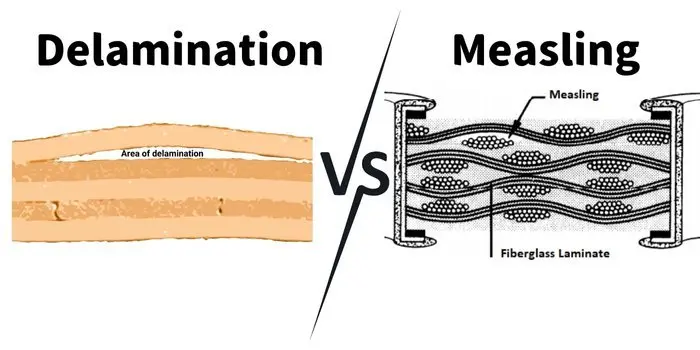
PCB Delamination vs Measling
Although delamination and measling are similar in appearance, they differ fundamentally. Delamination forms blisters that are caused by moisture trapped in the layers, which can severely affect the functionality of the board. Measling creates white spots within the PCB’s weave, either due to insufficient resin application or to mechanical stress. Minor measling is tolerable and common throughout a board’s lifecycle, but usually, it will not have any impact on performance unless it bridges conductors. Delamination, on the other hand, will almost always affect functionality negatively. Both problems have their roots in the manufacturing stage: delamination due to exposure to humidity, and inadequate bonding; and measling due to incorrect application of resin.
5 Common Causes of PCB Delamination
Delamination can stem from a variety of sources, including both manufacturing defects and operational stresses in the field. Understanding the root causes is key to preventing future occurrences. Common factors that contribute to PCB delamination include:
- Excessive Moisture
One of the main causes of PCB delamination is moisture. Even a small amount of moisture that becomes trapped in the board can lead to cracking when the PCB is subjected to high temperatures, as the moisture turns to steam and expands. In many cases, poor bonding or inadequate adhesive between the layers of the board enables moisture to seep in.
- Thermal Stress
Repeated heating and cooling leads to differences in thermal expansion and contraction between PCB layers. These mismatches generate mechanical stresses over time. Slow temperature changes during power cycling as well as rapid, localized heating can cause delamination.
- Low-quality Materials
Making PCBs with low-quality material can greatly increase the risk of delamination. These kinds of materials have defective resin formulations, inconsistent bonding of glass fibers, low peel strength, and insufficient copper adhesion, all of which decrease interlayer bond strength. As a result, the PCB is prone to absorbing more moisture, and experiencing more thermal stress during the manufacturing and assembly processes.
- Lamination Process Defects
Insufficient bonding, uneven resin flow, contamination and voids between layers can create weak points prone to delamination. This demonstrates the importance of closely controlling lamination press parameters.
- Excessive Bend Radii
Thin, flexible PCBs subjected to tight bends repeatedly experience focused interlayer stresses. Using adequate bend radii standards helps mitigate this.
Risks of PCB Delamination
- Signal Integrity Problems
Delamination will impact the inter-layer insulation, which leads to signal interference. It is especially problematic in high-speed digital circuits, leading to signal reflection, crosstalk, and impedance mismatch. As a result, it affects the signal integrity and stability.
- Electrical Performance Degradation
Delamination in PCBs results in reduced insulation resistance and increased leakage current, which would result in malfunctioning of the circuits, short circuits, or even the possibility of fire. It is a severe safety issue because these electrical failures may occur without warning.
- Mechanical Strength Reduction
Reduced interlayer bonding impairs the mechanical strength of the PCB. Delaminated boards are susceptible to physical stresses like vibration and bending and this reduces the durability and reliability of the product.
How to Prevent Delamination?
With knowledge of typical root causes, steps can be taken to minimize the risks of delamination in PCB designs and manufacturing:
- Material Selection
Research bonding films with maximum adhesive strength across full operating temperature range of end product, including thermal shock resistance. Ensure resin materials between layers have low coefficients of thermal expansion to match that of copper traces, reducing expansion mismatch strains. Require suppliers to provide lot testing data and certifications for resin quality, Tg, modulus, and elongation parameters.
- Moisture Control
Raw materials should be kept in storage rooms with desiccants to actively absorb humidity before use. Boards can be pre-baked prior to soldering to drive out any residual moisture. The assembly floor itself needs environmental controls like dehumidifiers to maintain optimal low moisture levels. Minimizing the time materials are exposed to ambient humidity is also important.
- Avoid Overheating
Overheating during the soldering process can lead to thermal stress, which in turn can cause delamination. Use appropriate soldering techniques, such as reflow soldering, and ensure that the temperature profiles are within the recommended range for both the components and the PCB.
- Process Controls
Closely control lamination heating/cooling rates, temperature dwell times, bonding pressure profiles, and resin flow parameters. Verify laminate quality through microsection analysis and bond strength destructive testing after pressing.
- Protective Coatings
Specify conformal coatings with high chemical, humidity, and temperature resistance to protect PCBs. Ensure complete coating coverage on all exposed surfaces to fully isolate from environmental ingress.
- Bend Radii Standards
Based on flex testing data, define and mandate minimum bend radii for PCB handling and installation to avoid overstress. Incorporate radius limits into assembly work instructions and quality inspection criteria.
Final Thoughts
PCB delamination is a very critical reliability issue that is influenced by the materials, manufacturing discipline, thermal management, and handling practices. Professional repair is not a cost-effective or reliable solution in most scenarios, although it is possible in exceptional situations.
Ultimately, the reduction of the risk of delamination is associated with the attentive selection of materials, strict process control, and efficient control of thermal exposure during PCB manufacturing and assembly.
FAQs about PCB Delamination
What causes PCB delamination during manufacturing?
PCB delamination is primarily caused by sudden rise in temperature, moisture absorption and CTE incompatibility between copper and laminate material especially in multilayer boards.
How can PCB delamination be detected before assembly?
PCB delamination can be detected through visual inspection to check whether the surface of the PCB contains any blisters or discoloration. It is also identifiable by using X-ray inspection that checks for internal layer separation.
Is PCB delamination repairable in multilayer PCBs?
In most cases, PCB delamination is not fully repairable because the separation of the internal layers compromises the structural integrity and reliability in the long run.
Does PCB baking prevent delamination?
PCB baking can effectively reduce the risk of delamination by removing absorbed moisture. However, it cannot completely prevent delamination because other factors also contribute to this issue.