Over the past few decades, IC packages have undergone continuous development. They play a critical role in guaranteeing the normal operation and longevity of these electronic components. IC packages, as the bridge connecting the internal circuitry with the external world, come in a diverse array of forms, each tailored to specific use cases and performance requirements. In this blog, we will introduce various IC package types and make comparisons among them. What’s more, we list key considerations when choosing the IC package type. Let’s read on.
What Is an IC Package?
IC package, with the full name of integrated circuit package, is an enclosure that encapsulates and shields an integrated circuit from unfavorable environmental factors such as moisture, corrosion, and dust. On the other hand, it facilitates the interconnection of integrated circuits with circuit boards and other components. ICs are tiny electronic devices comprising an extensive array of interlinked transistors, capacitors, resistors, and diverse electronic constituents housed on a single semiconductor substrate.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using IC Packages
Advantages
- Physical Protection: IC packages offer protection to sensitive components from physical damage, moisture, dust, and environmental factors, ensuring their longevity and reliability.
- Enhanced Reliability: Encapsulating delicate electronics within protective packages boosts the device’s reliability and extends its operational lifespan.
- Space Efficiency: IC packages have smaller dimensions than other individual components, which enables compact designs and increased component density on circuit boards.
- Simplified Assembly: Packaging facilitates easy and automated component assembly, leading to reduced manufacturing costs.
- Performance Improvement: IC packages can enhance device performance by reducing noise and providing effective thermal management.
Disadvantages
- Cost Factor: IC packages can be costlier than individual components, contributing to the overall device cost.
- Complexity: Certain IC packages are complex to handle, demanding specialized machinery and technical proficiency for both assembly and repair processe
- Limited Repairability: In the event of a component failure within the package, repair may be challenging or impossible without replacing the entire package.
- Package-Dependent Characteristics: The device’s performance may rely on the package used, and changing the package might alter the device’s behavior.
- Thermal Constraints: Certain IC packages may lack sufficient thermal management, leading to overheating and potentially reducing device performance and reliability.
Common IC Package Types
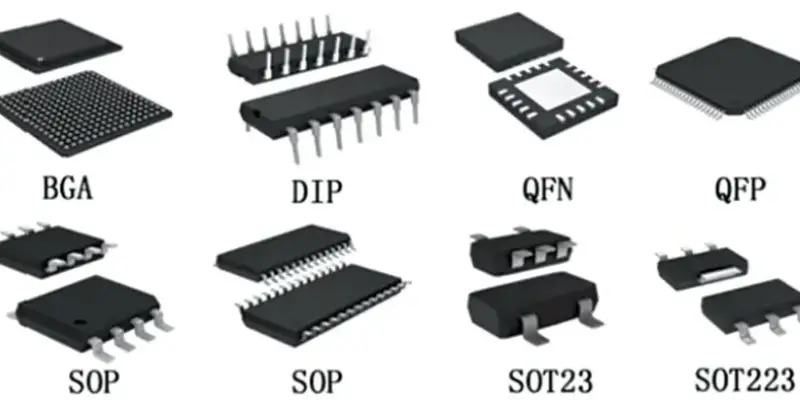

- Dual In-Line Package (DIP)
Dual In-Line Packages are one of the earliest and most common IC package types. They have two parallel rows of pins that easily plug into a socket-type connector on a PCB. DIP packages come in various pin counts, such as 8, 14, 16, 20, and more. While they are still used in some applications, they are becoming less prevalent due to more compact and efficient package types.
- Surface Mount Device (SMD)
SMD packages are popular due to their space-saving advantages. Unlike DIP packages, SMD packages do not have leads or pins for through-hole insertion. Instead, they have small solderable pads on the bottom surface of the package, allowing them to be soldered directly onto the PCB. Common SMD package types include Quad Flat Package (QFP), Small Outline Integrated Circuit (SOIC), and Thin Small Outline Package (TSOP).
- Ball Grid Array (BGA)
BGA packages are designed for high-performance applications. They have a series of solder balls on their bottom surface, replacing traditional pins or leads. The IC is mounted onto the PCB with the solder balls connecting it to the corresponding pads on the PCB. BGAs have the features of excellent electrical performance, thermal dissipation, and high pin counts, they are the first choice for microprocessors and GPUs.
- Quad Flat No-Lead (QFN)
QFN packages are similar to BGAs, but they have no exposed leads or balls on the bottom. Instead, they have small metal pads on the bottom, which are used for surface mounting on the PCB. QFN packages offer good thermal performance and a low profile, they are commonly used in the power management applications.
- Dual Flat No-Lead (DFN)
It is a type of surface mount integrated circuit packaging, This type of package has a flat, rectangular plastic body and exposed copper pads on the underside for soldering rather than leads that stick out from the sides. They are used for compact and lightweight devices, such as cell phones and consumer electronics.
- Chip Scale Package (CSP)
CSP packages are extremely compact and designed to be as close to the size of the integrated circuit as possible. They find frequent utilization in scenarios demanding constrained space, like in smartphones and wearable gadgets. CSPs are challenging to manufacture but are gaining popularity as technology advances.
| IC Package Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages | Common Applications |
| Dual In-Line Package (DIP) | One of the earliest and most common package types with two rows of pins | Easy insertion into socket connectors on PCB | Bulky, limited pin count, not ideal for modern designs | Legacy applications, simple circuits |
| Surface Mount Device (SMD) | Solderable pads on the bottom surface, space-saving | Compact, lightweight, suitable for automated assembly | Not ideal for high-power applications | General electronics, consumer devices |
| Ball Grid Array (BGA) | Solder balls on the bottom surface, high-performance | High pin count, excellent thermal dissipation | Difficult rework/repair, challenging to manufacture | Microprocessors, GPUs, high-speed applications |
| Quad Flat No-Lead (QFN) | No exposed leads, metal pads on the bottom, good thermal performance | Compact, low profile, better thermal characteristics | Difficult to inspect solder joints, not for high power | Power management ICs, RF applications |
| Dual Flat No-Lead (DFN) | The smaller variant of QFN, fewer pins | Compact, space-saving, lightweight | Limited pin count, challenging rework | Mobile devices, small electronics |
| Chip Scale Package (CSP) | Extremely compact, close to the size of the IC | Maximum miniaturization, space-efficient design | Challenging to manufacture, may require specialized PCB | Smartphones, wearables, space-constrained applications |
Choosing the Right IC Package Types
Choosing the right type of IC package is a critical decision that depends on several factors related to the specific application and design requirements:
Application Requirements: Different package types have different electrical and thermal characteristics, so when selecting an IC package, it is important to understand the requirements of the application, including required functionality, power dissipation, and heat dissipation. Only in this way can the most suitable type be selected.
Pin Count and I/O Requirements: Determine the required number of input/output (I/O) pins for your circuit. If your design requires a high pin count, consider package types like BGAs or QFPs. For lower pin counts, QFNs or smaller packages might be suitable.
Board Space and Layout Constraints: Evaluate the available board space and layout constraints. If you need to save space and have tight layout requirements, consider smaller packages like QFN or CSP.
Thermal Considerations: For high-power applications or devices that generate significant heat, choose IC package types with good thermal dissipation properties, such as BGAs.
Manufacturing and Assembly Considerations: Consider the ease of manufacturing and assembly when selecting the package type. Some packages, like BGAs, may require specialized equipment for soldering, while others, like DIPs or SMDs, are more straightforward to handle.
Cost Considerations: Different package types come at various price points. Choose a package that meets your requirements without unnecessarily inflating production costs.
Reliability and Durability: Consider the operating environment and durability requirements of the specific application. Some package types, like BGAs and QFNs, can offer improved reliability due to their solder joint configurations.
Design Flexibility and Future Upgrades: Consider the potential need for future upgrades or changes to the design. Package types with higher pin counts may allow for more flexibility in adding features or functionalities.
Key Takeaways
IC packaging plays a vital role in semiconductor manufacturing today. The protective and thermal benefits provided by IC packages have made them indispensable in modern electronics production. It is essential for industry players to understand different IC package types and choose the right one to improve the performance of electronic components. For queries spanning diverse types of IC packaging or matters concerning circuit boards, contact the experts at MOKO Technology now.