3D printing is a kind of additive manufacturing process that can create physical three-dimensional items based on digital models by successively laying down thin layers of materials. It is widely used for various industries including automotive, consumer products, construction, medical, and so on, as 3D printing can fabricate parts in different geometric shapes with high accuracy in a short time. With the constantly evolving 3D printings technology, the global 3D printing market is expected to reach $41 billion by 2026 as claimed by Acumen Research and Consulting.
Thus, we can get the conclusion that this technology would become mainstream in the near future and change the method of how we live and how we work.
How Does It Work
First, we need to design a virtual 3D model by using the computer-aided design (CAD) software, which can present clearly drawings and technical illustrations. Then, we need to slice the virtual model into hundreds or even thousands of thin layers by applying another software, and we call this process “slicing”.
Second, we need to convert the CAD file into an STL file so that it can be successfully recognized when we upload the file to the 3D printer.
Last, we will move to the printing process. The nozzle of the 3D printer will eject molten materials such as metal and plastic, and it moves both horizontally and vertically as instructed by the STL file, making sure that materials can be placed accurately. Such a process would be repeated to form every layer and ultimately the whole 3D product.
3D Printing Is Widely Used for Various Industries

- Automotive
3D printing has been applied in the automotive industry for a long time, it can be used to print tools, jigs and fixtures, and to test form and fit, making sure all car parts can be operated as expected. In addition, many automakers use this technology to restore old cars whose parts were out of production already.
- Aviation
3D printed parts are featured with lightweight and high precision, more importantly, they can be made in complicated shapes, so 3D printing is widely used in the aviation industry. Using traditional manufacturing methods to create a complex part requires welding different individual components together, while 3D printings can create an item as one whole component, which would reduce the material wastage and shorten the production time.
- Construction
3D printing has wide applications in the construction industry including private, commercial, and public sectors. 3D printings can present the works of architectural designers in the shortest time, and it is also convenient for them to make some modifications and adjustments. In addition, many real estate developers will also use this technology to show the buildings so that customers can observe them more clearly.
- Consumer Products
3D printing technology has a big market in consumer products, from the things we used in daily life such as glasses, shoes to luxury like jewelry. Take the glasses as an example, not only the frame can be printed, but also the lenses can be printed. Traditionally, we make lenses by removing the extra materials, but 3D printing can reduce material waste when making lenses.
- Healthcare
3D printing technology can be used to create different models for medical use, such as in dentistry, to print crowns and braces. Implants like hip and knee joints can also be made, as well as hearing aids, prosthetics, and more, which will aid surgeons in their work and patient recovery. The application of 3D technology in this industry will promote the progress of medicine and improve people’s health.
Types of 3D Printing Processes
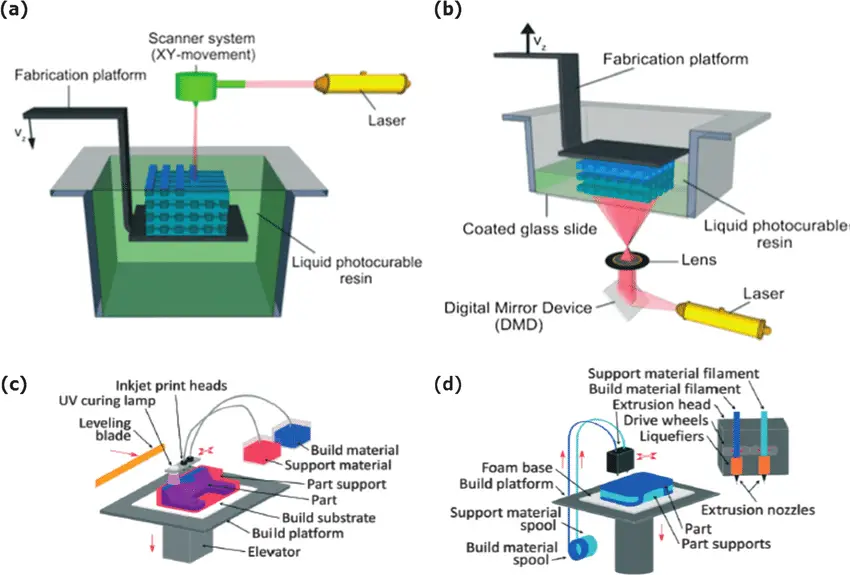
Binder jetting is a kind of 3D printing process that requires two materials during manufacturing: the base material powder and the binder. We use the binder to bond powders selectively, and the powder particles would be bonded layer by layer to form the final part. The raw materials of binder jetting can be metals, sand, and ceramics as well.
This process is featured with high efficiency, we can add the number of print head holes to speed up the production. In addition, it can be used to print kinds of parts by changing the properties of materials and the ratio of two materials, which is really versatile.
Fused deposition modeling, also known as FDM, creates 3D parts by depositing molten material selectively based on the previously designed virtual 3D model. Normally, thermoplastic polymers are used as raw materials including ABS, PC, PLA, TPU, and so on. These materials are presented in the form of filaments that can be combined layer by layer to form the shape of the 3D parts. It is the most widely used 3D printing process, we can find this process in different industries and applications such as consumer products, automotive, and medical.
Selective laser sintering is a 3D printing process widely used to print parts for medical devices, electronics, and cars. It applies laser beams to sinter powder selectively according to the CAD data, and then the sintered powder would be bonded layer to layer to make the three-dimension parts. A variety of materials are available for selective laser sintering such as nylon, elastomeric thermoplastics, and polystyrene.
Stereolithography is a type of 3D printing process with high resolution and precision, the tolerance of stereolithography parts is about 0.05 mm. In addition, it is featured with smooth surface finishes and material versatility. The working principle of stereolithography is to use laser and photopolymerization to harden the liquid resin and form the final solid 3D parts. This 3D printing process is perfect for manufacturing highly accurate parts like some functional parts and presentation models.
How to Select the Suitable 3D Printing Processes
It would be a little bit difficult for us to select the right printing process for creating a part, as there are kinds of 3D printing processes available, and sometimes not only one process is suitable, maybe two or three processes are all workable. But below are some considerations that should be taken before making our decisions:
First, the material properties required for the parts including the strength, hardness, and so on. As we know that the raw materials of various processes are different, therefore, it is necessary to take the characteristics of the material into consideration when selecting the process.
Second, the requirements about functions and aesthetics. For example, do you have requirements about heat resistance and strength of the part, or do you require a very smooth surface?
Last, the capabilities of the 3D printing process, which may include high precision, build size, and so on.
What Benefits Can 3D Printing Bring to Us?
Reduced Costs
3D printing can reduce the manufacturing cost significantly for the following reasons:
First of all, 3D printing is all performed by machines. Unlike traditional production processes, a large number of employees are required to operate different machines and equipment, thus, a large part of labor costs can be saved. In addition, although the cost of up-front purchase of equipment is relatively expensive, the high productivity of 3D printing is enough to offset the cost of equipment. Lastly, 3D printing is an additive process, which means there is no material wasted during the manufacturing process that can reduce the cost of raw materials as well.
Short Turnaround Time
Another benefit that 3D printing can bring to us is that it allows us to make 3D parts and products in a short turnaround time. We can finish the design very quickly even some complicated designs by using the CAD software, and the virtual 3D model can be converted to a physical 3D model in just a few hours. While the traditional methods may need to take a few weeks or even months to finish the whole process from the design, rapid prototyping to the final product manufacturing.
Tool-less
For industrial manufacturing, the production of tools is a very requires a lot of development costs, time, and labor. This problem can be well resolved by using 3D printing, which can eliminate the need for tool production. During the design stage, the engineers can design products and components in a specific way that can avoid assembly requirements. Tool-less is a highlight of 3D printing that can further reduce the costs needed for assembly processes.
Sustainability
3D printing is environmentally friendly as it has high material utilization during the production process that can reach 90% for standard materials. And 3D printed parts are light and durable that can be used for a long time, which can improve sustainability significantly. In addition, 3D printing can solve the problem of inventory build-up, because of fast production times, suppliers do not need to manufacture parts long in advance and store them in warehouses.
Design Flexibility
3D printing supports the use of a variety of materials, which helps to break down material limitations, giving engineers more options to design more creative products. On the other hand, this technology can be used to manufacture parts in different geometric shapes from simple to complex.
Working with MOKO to Start Your 3D Printing Projects
MOKO Technology specializes in kinds of 3D printing processes such as binder jetting, stereolithography, fused deposition modeling, and selective laser sintering. MOKO utilizes the industry-leading 3D printers that allow us to manufacture parts with high precision and productivity. On the other hand, we have rich experience in this area and our experts would work with you closely throughout the project, making sure that each step goes smoothly.
For 3D printed parts, kinds of metal and plastic materials are available at MOKO, which gives us more choices at the designing stage. We are capable of offering different 3D printing solutions for different applications and industries, such as automotive, aviation, medical, consumer products, etc. We are confident to provide the best 3D printing services to our clients, just send us your 3D CAD file, and you will see how we can set you apart from others.